
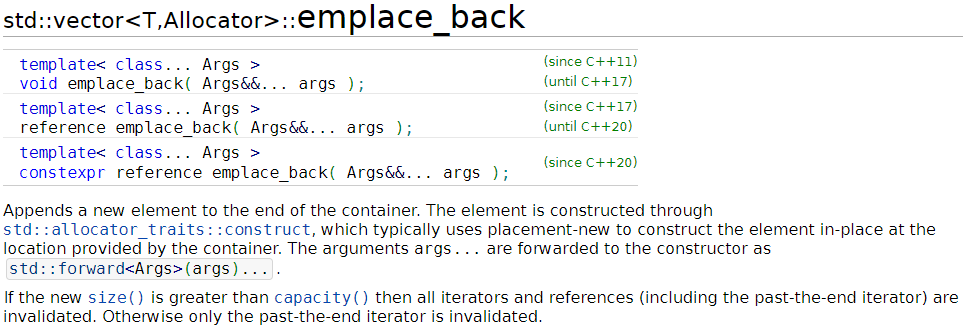
push_back과 emplace_back은 완전히 같다.
l-value가 들어오면 copy를 수행한다.
r-value가 들어오면 move를 수행한다.
emplace_back은 여기에 추가적으로 std::allocator_traits::construct를 제공한다.
이말이 무슨 뜻이냐면 생성자 파라미터만 적으면 copy,move를 하지 않고 추가해준 공간에 직접 객체를 생성한다는 이야기이다.
class Test {
public:
Test() : a(0) {
cout << "Test() " << this << endl;
}
explicit Test(int a) : a(a) {
cout << "Test(int a) " << this << endl;
}
Test(const Test& rhs) {//복사 생성
cout << "Test(const Test& rhs) " << this << "\trhs : " << &rhs << endl;
a = rhs.a;
}
Test(Test&& rhs) noexcept {//이동 생성
cout << "Test(Test&& rhs) " << this << "\trhs : " << &rhs << endl;
a = rhs.a;
}
Test& operator=(const Test& rhs) {
cout << "operator=(const Test& rhs) : " << this << "\trhs : " << &rhs << endl;
}
Test& operator=(Test&& rhs) noexcept {
cout << "Test& operator=(Test&& rhs) " << this << endl;
return *this;
}
~Test() {
cout << "~Test() " << this << endl;
}
int a;
};
int main()
{
vector<Test> vt;
vt.reserve(10);
cout << "(1) vt.push_back(t)" << endl;//l-value
Test t;
t.a = 10;
vt.push_back(t);
cout << endl;
cout << "(2) vt.emplace_back(f)" << endl;//l-value
Test f;
f.a = 20;
vt.emplace_back(f);
cout << endl;
cout << "(3) vt.push_back(Test())" << endl;//r-value
vt.push_back(Test(30));
cout << endl;
cout << "(4) vt.emplace_back(Test())" << endl;//r-value
vt.emplace_back(Test(40));
cout << endl;
cout << "(5) vt.emplace_back(constructor)" << endl;//constructor
vt.emplace_back(50);
cout << endl;
cout << "(6) vt element" << endl;
for (auto& item : vt) {
cout << item.a << endl;
}
}
결과

